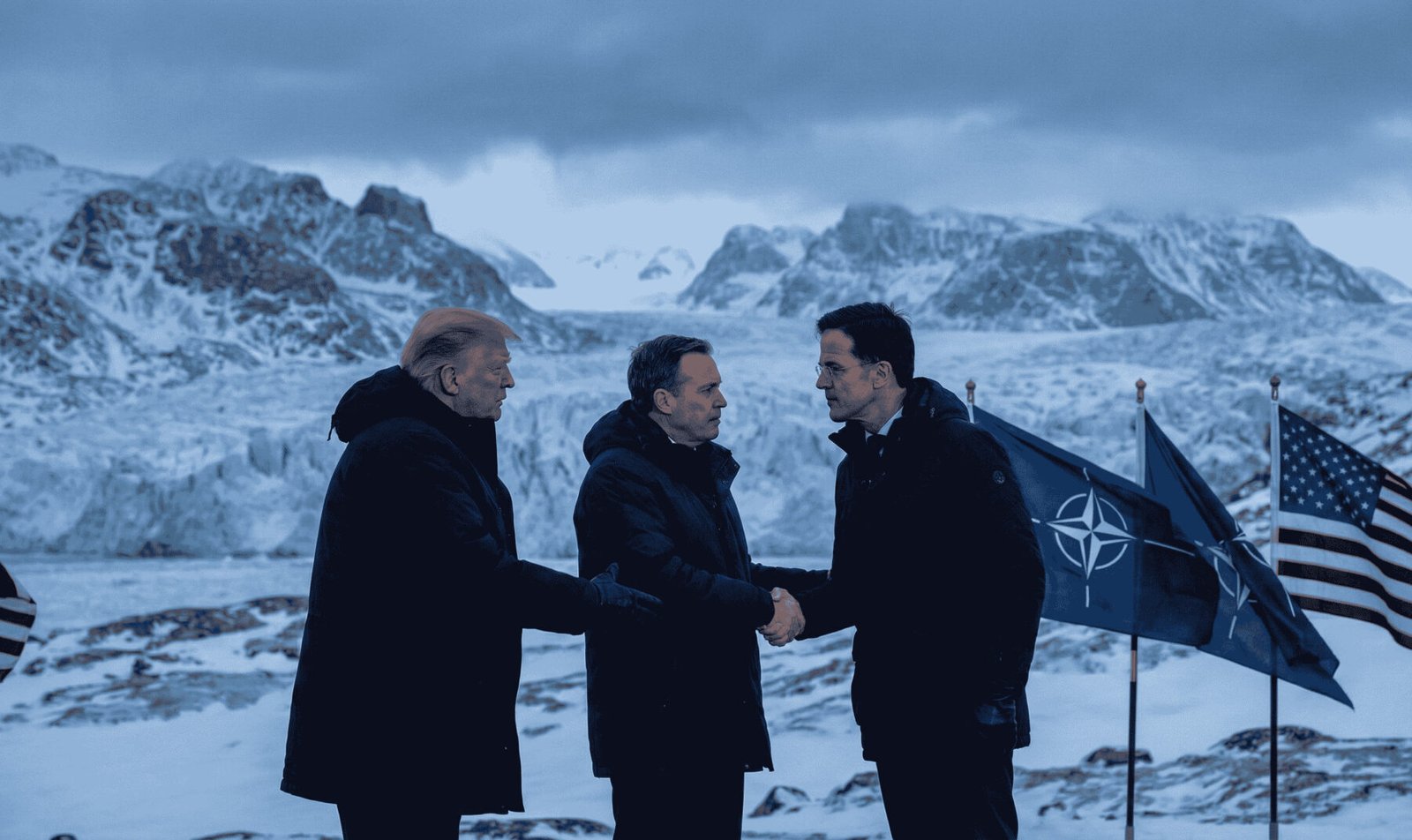
The announcement represents a marked departure from Trump’s earlier hardline stance — including threats of tariffs on European allies — and reflects growing geopolitical focus on the Arctic, where the strategic importance of Greenland has surged amid global competition with Russia and China.
In this in-depth analysis, we explore why this matters, what the “framework” could mean, how European nations reacted, and what this signals about future Arctic diplomacy.
Table of Contents
A Sudden U-Turn: From Tariffs to Framework Deal
Just days earlier, Trump had stirred diplomatic tensions by threatening to impose steep tariffs — initially starting at 10% from February 1 and rising to 25% by June — on eight European NATO members that resisted his push regarding Greenland’s future.
Those nations included key U.S. allies — Denmark, France, the United Kingdom, Germany, Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands, and Finland — all of which rebuffed any suggestion that Greenland could be transferred or sold.
However, on January 21, 2026, Trump stunned world leaders by announcing that the tariff threats were being dropped entirely. He wrote on his social platform that after a “very productive meeting” with NATO’s secretary-general, the two sides had formed a framework of a future deal regarding Greenland and the broader Arctic region — and based on that understanding, tariff imposition was off the table.
This reversed stance came only hours after Trump had publicly ruled out military force to seize Greenland, a move that had alarmed many European governments and drawn fierce criticism over its implications for NATO unity.
Why Greenland Matters: Strategic, Economic, and Security Factors
1. Arctic’s Growing Geopolitical Importance
Greenland — while geographically remote — sits at the crossroads of Arctic security, energy, and military strategy. Its location near the Arctic Circle makes it a linchpin in any future contest for influence among global powers, especially as polar ice melts and new shipping routes and resource prospects open up.
For decades, Greenland has been part of the Kingdom of Denmark and hosts a significant U.S. military presence under longstanding defense agreements. But Trump’s renewed focus on the island triggered a debate about whether Washington could expand its strategic footprint there.
2. The “Golden Dome” Defense Initiative
Trump repeatedly tied the Greenland issue to national security, referencing the development of a proposed missile defense network dubbed the “Golden Dome” system — a high-level defense structure said to involve space-based systems. Discussions about this program continue, and they were explicitly referenced by Trump in his announcement about the future framework.
What Trump’s Framework Might Actually Include
Despite Trump’s assertion of having reached a framework worth celebrating, details remain vague. Neither NATO nor European officials have released a clear text of the agreement, and there is no indication that any transfer of territory was negotiated.
Here’s what is likely part of the framework or discussion:
1. Increased Arctic Security Collaboration
According to NATO Secretary-General Mark Rutte, the framework emphasizes strengthened NATO cooperation to secure the Arctic region. Rutte stated the pact would call on member nations to step up security measures in the North in 2026, even involving nations without Arctic borders.
This focus on Arctic security doesn’t equate to territorial concessions. Rather, it signals an attempt to unify NATO’s efforts against possible Russian and Chinese influence in the polar region — a priority for many allied governments.
2. Continued Dialogue on Defense Facilities
While Denmark controls Greenland, the United States already operates defense bases there, including important early-warning radar and military infrastructure. The proposed framework could outline expanded cooperation on defense facilities and investment — not ownership transfer — though details are limited.
3. Zero Tariffs for Now — But Future Talks Continue
The most immediate outcome is that tariffs that were scheduled to begin on February 1 have been canceled, in part to ease tensions and preserve transatlantic cooperation.
However, continued talks are expected among U.S. officials — including Vice President J.D. Vance, Secretary of State Marco Rubio, and special envoy Steve Witkoff — to flesh out specifics on Arctic collaboration.

European Reaction: Cautious Relief and Firm Resistance
European leaders broadly welcomed the de-escalation that came with the tariff cancellation — but they also made it clear that sovereignty over Greenland is not negotiable.
Denmark’s Firm Stance
Denmark’s Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen reiterated that Greenland’s sovereignty is sacrosanct and cannot be bought or negotiated away, even under the umbrella of NATO cooperation. Her government insists that any discussions must respect the rights of Greenland’s people and Denmark’s territorial integrity.
Danish officials were particularly firm that NATO’s secretary-general does not have the authority to negotiate territorial changes for Greenland — underscoring that Copenhagen and Nuuk must lead any future talks.
European Union and NATO Allies Push Back
Leaders from several European nations had harshly criticized Trump’s earlier tariff threat, warning that such coercion could undermine NATO unity. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen even proposed a coordinated package to strengthen Arctic security cooperation independent of U.S. pressure.
Countries like the United Kingdom and Germany reiterated that any decisions about Greenland’s future must involve Greenlanders themselves, reinforced by calls within the EU for deeper strategic cooperation in the Arctic.
This response reflects a broader caution: while Europe appreciates the easing of trade tensions, many capitals remain wary about elevated U.S. pressure tactics and insist that alliance solidarity must be based on shared values and mutual respect.
Transatlantic Relations: A Test of Trust
The Greenland episode has spotlighted deeper questions about U.S.–Europe relations and NATO cohesion:
- Trump’s initial approach — threatening tariffs to influence sovereign territory — unsettled many allied capitals and raised constitutional questions about alliance dynamics.
- The swift rollback and emphasis on a vague framework bears the hallmarks of transactional diplomacy, where political calculations intertwine with strategic goals.
European officials now argue that this episode highlights the need for stronger European strategic autonomy — particularly in the Arctic — and a reassessment of how much Europe should depend on U.S. leadership for regional security matters.
Implications for the Future
1. Arctic Security Will Rise on NATO’s Agenda
With Moscow increasingly assertive and Beijing showing interest in polar shipping routes and resources, NATO is likely to prioritize Arctic security more than ever. This could include joint exercises, intelligence sharing, and infrastructure upgrades in the north — but always within the bounds of sovereign authority.
2. Trade Relations Between U.S. and Europe May Still Be Fragile
Although tariffs are off the table for now, the underlying tensions over trade leverage haven’t disappeared. Experts warn that future trade disputes could resurface if diplomatic trust isn’t rebuilt.
3. Greenland’s Role in Global Politics Is Growing
Previously viewed as a remote Arctic island, Greenland is now firmly on the global geopolitical map. Its strategic importance — for defense, shipping, and natural resources — ensures that it will remain a focus for policymakers in Washington, Copenhagen, and beyond.
Conclusion: A Moment of Diplomacy Amid Uncertainty
Donald Trump’s unexpected withdrawal of tariff threats and his announcement of a framework for a future Arctic deal with NATO signals both a de-escalation of immediate tensions and a broader strategic pivot toward Arctic security cooperation.
However, the absence of concrete details and the firm resistance from European allies underscore that real progress will depend on respectful diplomacy and shared objectives rather than unilateral leverage.
As global power dynamics evolve, the Arctic — once a frozen frontier — has become one of the most consequential arenas in 21st-century geopolitics. The Greenland episode may be just the beginning of how nations navigate this complex terrain in the years to come.